- 01792-220191, 09839141955, 06390845955
- SCO No. 2 & 3, Block-B;Office No.-249A; 2nd Floor, Motia Plaza Baddi-173205; Distt. Solan (H.P.)
- Home
- Protein Powder
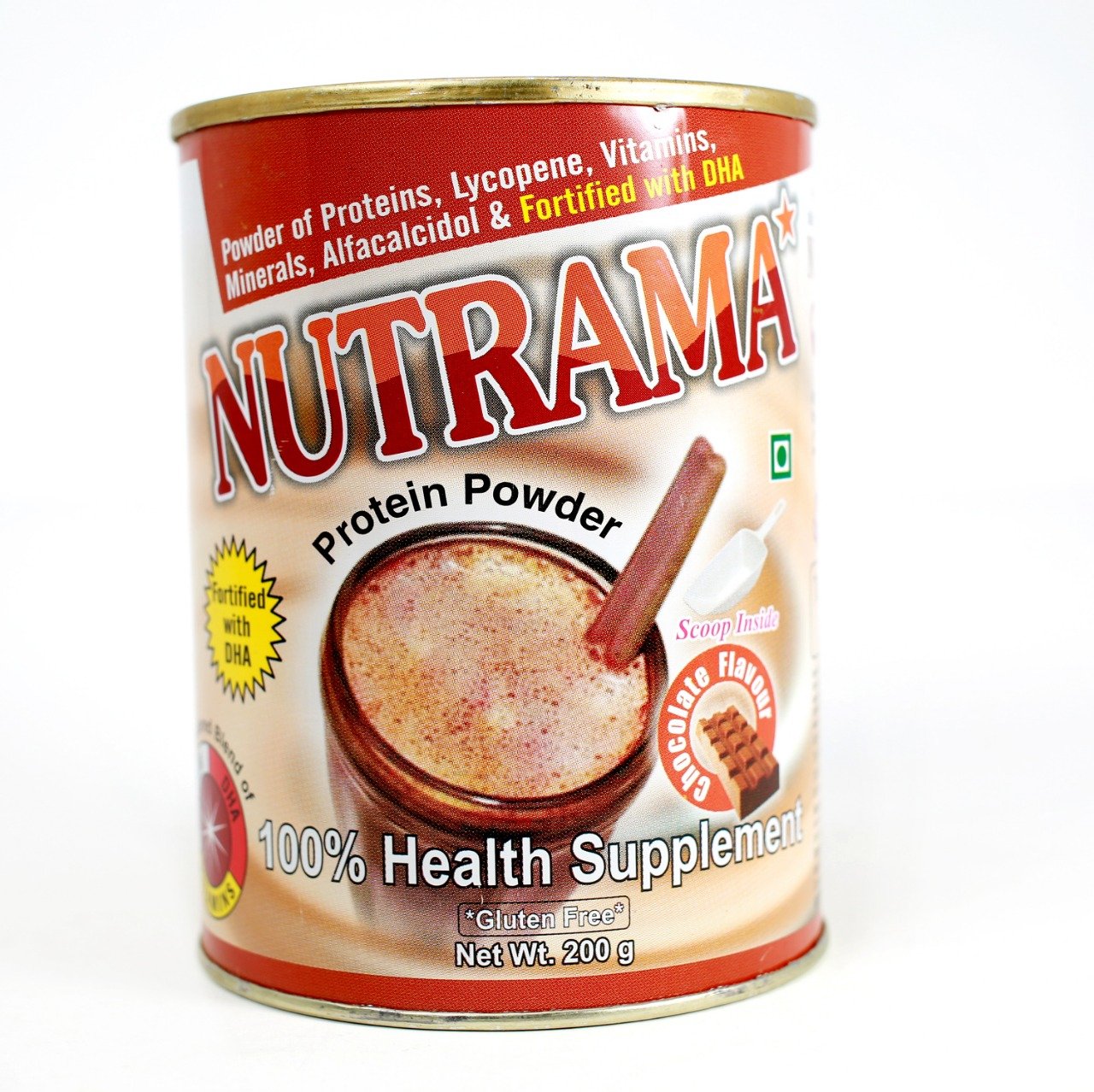
- NUTRAMA (CHOCLATE FLAVOUR) (FOOD PRODUCT)

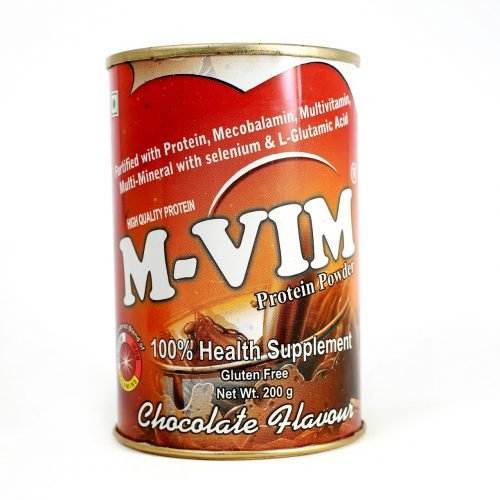
M-VIM (CHOCOLATE FLAVOUR) (FOOD PRODUCT)
September 19, 2019
ANAIKACIN-100
September 19, 2019NUTRAMA (CHOCLATE FLAVOUR) (FOOD PRODUCT)
| Brad Name | Nutrama (Choclate Flavour) (Food Product) |
| Composition | Powder of Proteins, Lycopene, Vitamins, Minerals, Alfacalcidol & Fortified with DHA Protein Powder |
Powder of Proteins, Lycopene, Vitamins, Minerals, Alfacalcidol & Fortified with DHA Protein Powder
Whey protein is the protein contained in whey, the watery portion of milk that separates from the curds when making cheese. When protein is commonly used for improving athletic performance and increasing strength, but evidence to support these uses is mixed. Whey protein is also used to reverse weight loss in people with HIV and to help prevent allergic conditions in infants.
How does it work?
Whey protein is a source of protein that might improve the nutrient content of the diet. Whey protein might also have effects on the immune system.
Dosage
ADULTS
BY MOUTH:
- For HIV/AIDS-related weight loss: 8.4-84 grams of whey protein per day, 2.4 grams/kg per day in a high-calorie formula, or 42-84 grams per day in a glutamine-enriched formula.
- For red, scaly skin (plaque psoriasis): 5 grams per day of a specific whey protein extract product.
Possibly Effective for
- Athletic performance. Most research shows that taking whey protein in combination with strength training increases lean body mass, strength, and muscle size in healthy young adults. Taking whey protein also appears to improve running speed and recovery from exercise in untrained adults. Whey protein seems to work as well as soy, chicken or beef protein for increasing muscle strength.
- Eczema. Research shows that infants who consume whey protein by mouth during the first 3-12 months of life have a lower risk of developing red, itchy skin by the age of 3 years.
- A condition associated with an increased risk for developing allergic reactions (atopic disease). Research shows that infants who consume whey protein by mouth during the first 3-12 months of life are less likely to be prone to allergies and allergic reactions compared to infants who receive standard formula. However, taking why protein might not be helpful for treating atopic diseases once they develop.
- Weight loss in people with HIV/AIDS. Some research shows that taking whey protein by mouth can help decrease weight loss in people with HIV.
- Red, scaly skin (plaque psoriasis). Some evidence shows that taking a specific whey protein extract daily for 8 weeks can reduce psoriasis symptoms.
Side effects
Whey protein is LIKELY SAFE for most children and adults when taken by mouth appropriately. High doses can cause some side effects such as increased bowel movements, nausea, thirst, bloating, cramps, reduced appetite, tiredness (fatigue), and headache.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: There is not enough reliable information about the safety of taking whey protein if you are pregnant or breast feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Drug interaction
Levodopa interacts with WHEY PROTEIN
Whey protein might decrease how much levodopa the body absorbs. By decreasing how much levodopa the body absorbs, whey protein might decrease the effectiveness of levodopa. Do not take whey protein and levodopa at the same time.
- Alendronate (Fosamax) interacts with WHEY PROTEINWhey protein can decrease how much alendronate (Fosamax) the body absorbs. Taking whey protein and alendronate (Fosamax) at the same time can decrease the effectiveness of alendronate (Fosamax). Don’t take whey protein within two hours of taking alendronate (Fosamax).
- Antibiotics (Quinolone antibiotics) interacts with WHEY PROTEINWhey protein might decrease how much antibiotic the body absorbs. Taking whey protein along with some antibiotics might decrease the effectiveness of some antibiotics. To avoid this interaction take whey protein supplements at least one hour after antibiotics. Some of these antibiotics that might interact with whey protein include ciprofloxacin (Cipro), enoxacin (Penetrex), norfloxacin (Chibroxin, Noroxin), sparfloxacin (Zagam), trovafloxacin (Trovan), and grepafloxacin (Raxar).