- 01792-220191, 09839141955, 06390845955
- SCO No. 2 & 3, Block-B;Office No.-249A; 2nd Floor, Motia Plaza Baddi-173205; Distt. Solan (H.P.)

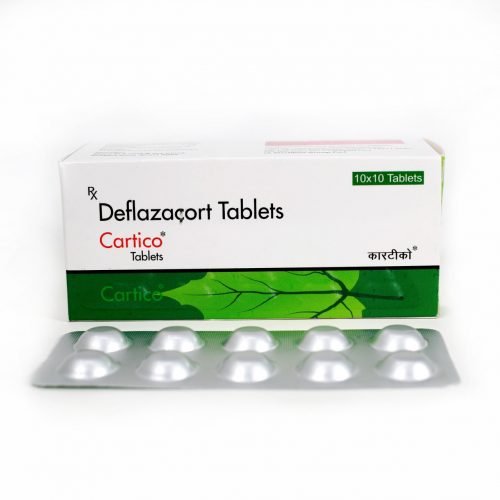
SANSYLATE-500
September 19, 2019
SANTOCAL-PLUS
September 19, 2019SANTOCAL-500
| Brad Name | Santocal-500 |
| Composition | Calcium Carbonate 1250 mg + Magnesium Hydroxide 240 mg + Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate 11 mg + Vitamin D3 200IU Tablets |
Calcium carbonate 1250 mg + magnesium hydroxide 240 mg + zinc sulphate monohydrate 11 mg + vitamin D3 200 I.U
It is used to prevent or treat low blood calcium levels in the people who do not get enough calcium from their diets. It may be used to treat conditions caused by low calcium levels such as bone loss, weak bones, decreased activity of the parathyroid gland and a certain muscle disease. It may also be used in the women
Calcium carbonate is converted to calcium chloride by gastric hydrochloric acid in stomach, calcium as such prevents bone loss in postmenopausal women and is associated with a modest reduction in fracture risk.
Magnesium is essential for enzyme activity, calcium and potassium uptake, nerve transmission, bone formation and metabolism of carbohydrates and minerals. It is magnesium, which helps form hard tooth enamel, resistant to decay. Zinc is required for the normal growth and tissue repair.
Vitamin D3 is a form of vitamin D. It is also called as Cholecalciferol. Vitamin D exerts it`s action by influencing calcium homoeostasis. It increases the intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphate. It increases the synthesis of a carrier protein for calcium called “calbindin” or calcium binding protein. It helps in bone mineralization.
Indications
- Calcium deficiency
- Osteoporosis in males
- Post-menopausal osteoporosis.
- Rickets
- Osteocalcaemia
Dosage
Adult : 1 tablet / day and if needed dose can be increased by 1 capsule every 2 week
Contraindications
Contraindicated in patients with hypercalcaemia and to those with the evidence of vitamin D toxicity.
Hypersensitive to any ngredient
Precautions
- Excessive dosage of the tablet may induce hypercalcaemia and in some instances hypercalciuria. Therefore early in the treatment during dosage adjustment, serum calcium should be determined periodically at regular intervals
- Excessive intake of zinc may lead to overdosage symptoms like nausea, severe vomiting, dehydration, restlessness and sideroblastic anaemia
- It should be avoided in patients on digitalis because hypercalcaemia in such patients may precipitate cardiac arrhythmias
Side effects
Weakness, headache,somnolence, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, constipation, muscle pain, bone pain, metallic taste, dehydration, restlessness and sideroblastic anaemia
Drug interaction
- Antacids: Hypermagnesemia may develop in patients on renal dialysis who take magnesium containing antacids.
- Digitalis glycosides: May precipitate cardiac arrhythmias due to hypercalcemia.
- Verapamil: Atrial fibrillation may occur.
- Cholestyramine: Intestinal absorption of Vitamin D may be reduced.
- Mineral Oil: Prolonged use of mineral oil may result in reduced absoprtion of Vitamin D.
- Phenytoin, Barbiturates: Half life of vitamin D may be reduced.
- Thaizide diuretics: Hypoparathyroid patients on Vitamin D may develop hypercalcemia due to thiazide diuretics.
- Fluoroquinolones, Tetracyclines: Decreased GI absorption and serum levels of some fluoroquinolone.
- Pencillamine: Reduced absorption of zinc.
- Iron: Reduced absorption of iron and vice versa
- Bran products (including brown bread) and some foods (e.g. proteins, phytates, some minerals) may decrease zinc absorption