- 01792-220191, 09839141955, 06390845955
- SCO No. 2 & 3, Block-B;Office No.-249A; 2nd Floor, Motia Plaza Baddi-173205; Distt. Solan (H.P.)

SANTOCAL-500
September 19, 2019
SANTROX-150
September 19, 2019SANTOCAL-PLUS
| Brad Name | Santocal-Plus |
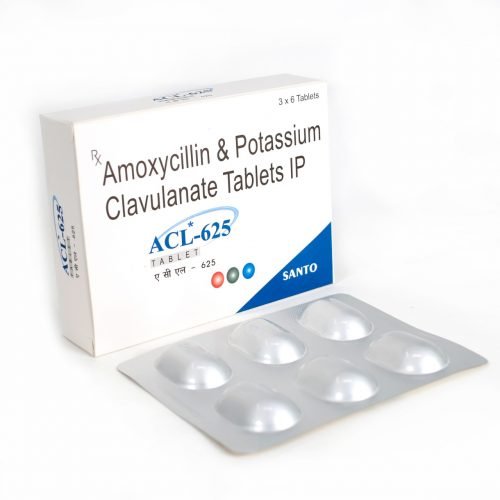
| Composition | Calcitriol 0.25 mcg + Magnesium 100 mg + Calcium Citrate 1000 mg + Zinc 7.5 mg Tablets |
Calcitriol 0.25 mg + Magnesium 100 mg + Calcium citrate 1000 mg + Zinc 7.5 mg
Calcitriol must be adequate for optimal absorption of calcium
Magnesium plays an essential role in the proper functioning of the nerves, muscles and heart. It plays an important role in uterine muscle tone during pregnancy and labor.
Calcium citrate is highly soluble and easy for body to utilize. Due to its high bioavailability, calcium citrate is preffered over calcium carbonate. It is essential for the functional integrity of of the nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems. Zinc helps your immune system and plays a role in making DNA and proteins. It is required for the functioning of enzymes that produce collagen and other connective proteins needed for bone matrix
Indications
- Pregnancy and lactation
- Osteoporosis
- Fracture
- Hypocalcemic conditions
- Osteomalacia
Dosage
1 tablet twice a day
Contraindications
- Hypercalcemia, primary or secondary
- Hypercalciuria
- Renal calculi, calcium (risk of exacerbation)
- Sarcoidosis (may potentiate hypercalcemia)
- Ventricular fibrillation
Precautions
- Careful titration is recommended to prevent hypercalcemia, which has been reported with doses above 2 grams of calcium ion a day
- Use of calcium citrate in patients with dehydration or electrolyte imbalance may increase the risk of hypercalcemia
- Use with cautions in patients on digitalis, because hypercalcemia may precipitate cardiac arrhythmias
- Fecal excretion of calcium may be increased in patients with chronic diarrhea or malabsorption, although such patients commonly need calcium supplements
- Use with caution in patients on digitalis, with CHF or renal failure
- No other calcium supplements should be given concurrently
Side effects
Weakness, headache,somnolence, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, constipation, muscle pain, bone pain, metallic taste, dehydration, restlessness and sideroblastic anaemia, hypercalcemia
Drug interaction
- Antacids: Hypermagnesemia may develop in patients on renal dialysis who take magnesium containing antacids.
- Digitalis glycosides: May precipitate cardiac arrhythmias due to hypercalcemia.
- Verapamil: Atrial fibrillation may occur.
- Cholestyramine: Intestinal absorption of Vitamin D may be reduced.
- Mineral Oil: Prolonged use of mineral oil may result in reduced absoprtion of Vitamin D.
- Phenytoin, Barbiturates: Half life of vitamin D may be reduced.
- Thaizide diuretics: Hypoparathyroid patients on Vitamin D may develop hypercalcemia due to thiazide diuretics.
- Fluoroquinolones, Tetracyclines: Decreased GI absorption and serum levels of some fluoroquinolone.
- Pencillamine: Reduced absorption of zinc.
- Iron: Reduced absorption of iron and vice versa
- Bran products (including brown bread) and some foods (e.g. proteins, phytates, some minerals) may decrease zinc absorption