- 01792-220191, 09839141955, 06390845955
- SCO No. 2 & 3, Block-B;Office No.-249A; 2nd Floor, Motia Plaza Baddi-173205; Distt. Solan (H.P.)

CARTICO
September 19, 2019
CHENIM
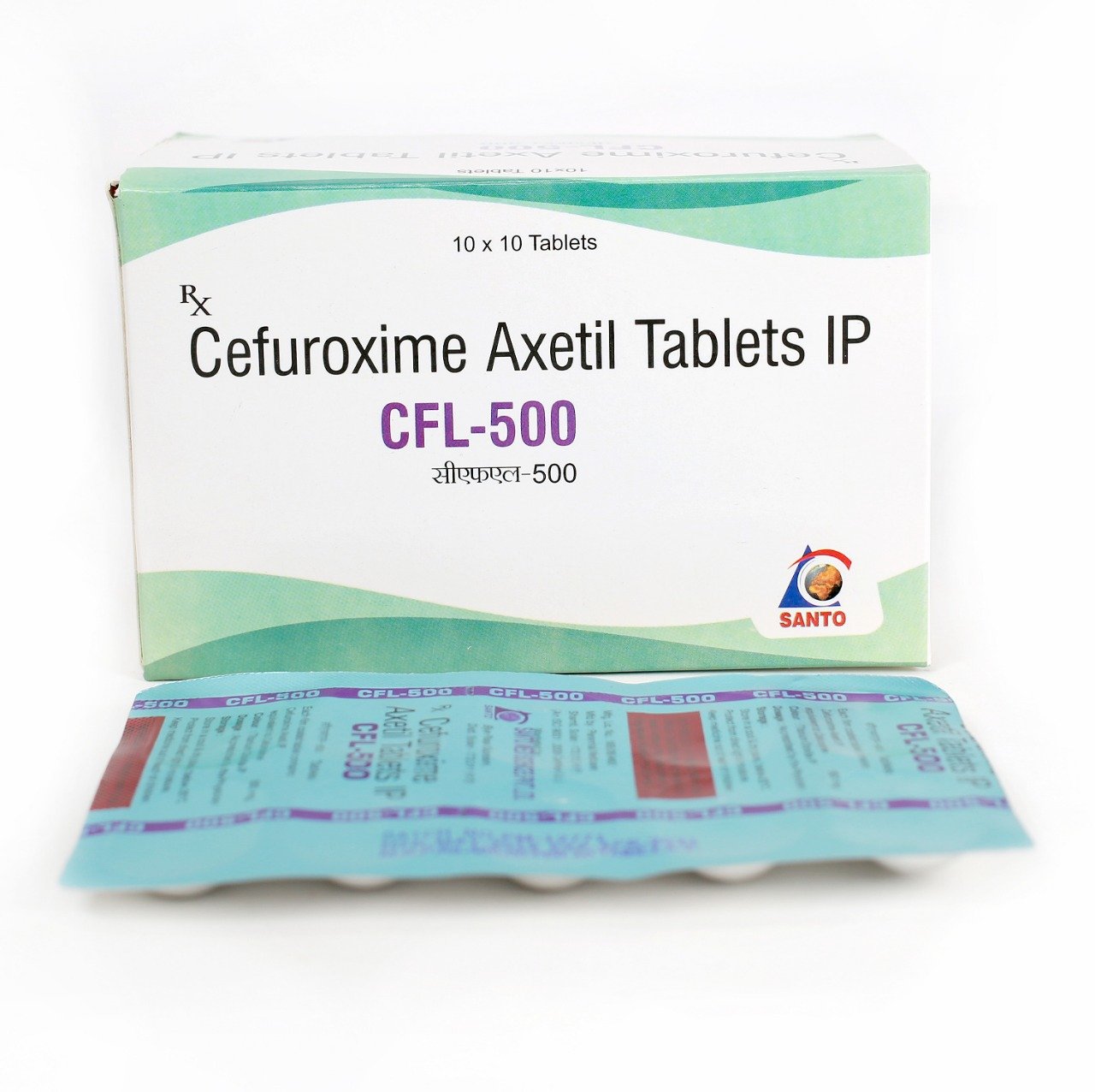
September 19, 2019CFL-500
| Brad Name | CFL-500 |
| Composition | Cefuroxime Axetil 500 mg Tablets |
Cefuroxime proxetil 500 mg
CFL (Cefuroxime) is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic, chemically similar to penicillin. It stop or slow the growth of bacterial cells by preventing bacteria from forming the cell wall that surrounds each cell. The cell wall protects bacteria from the external environment and keeps the contents of the cell together. Without a cell wall, bacteria are not able to survive. CFL is effective against a wide variety of bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, E. coli, N. gonorrhea, and many others. The FDA approved cefuroxime in December 1987.
Indications
- Pharyngitis/tonsillitis
- Acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis
- Chronic bronchitis
- Skin and skin structure infections
- UTI
- Otitis media
Dosage
- For chronic bronchitis -500 mg b.i.d for 10 days
- For secondary bacterial infections of acute bronchitis – 500 mg b.i.d for 5-10 days
- Early lyme disease – 500 mg for b.i.d for 10-20 days
contraindications
Cefuroxime Axetil products are contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
Precautions
Cephalosporins, including Cefuroxime Axetil, should be given with caution to patients receiving concurrent treatment with potent diuretics because these diuretics are suspected of adversely affecting renal function. Cefuroxime Axetil, as with other broad-spectrum antibiotics, should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a history of colitis.
Risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antimicrobial therapy, and patients previously stabilized on anticoagulant therapy. Modify dosage in patients with severe renal impairment, prolonged use may result in superinfection; use with caution in patients with a history of penicillin allergy, especially IgE-mediated reactions (eg, anaphylaxis, urticaria); may cause antibiotic-associated colitis or colitis secondary to C. difficile
Side effects
Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, headache, rash, hives, vaginitis, and mouth ulcers. Allergic reactions, severe skin reactions, anemia, and seizures also may occur. Since cefuroxime is chemically related to penicillin, patients allergic to penicillin may develop an allergic reaction (sometimes even anaphylaxis) to cefuroxime. Cefuroxime like other antibiotics can alter the colon’s normal bacteria, leading to overgrowth of a bacterium called Clostridium difficile. Overgrowth of this bacterium leads to the release of toxins that contribute to the development of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, which may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal pseudomembranous colitis
DRUG INTERACTION
- Probenecid increases the concentration of cefuroxime in the blood. Drugs that reduce acidity in the stomach (for example, antacids, H2-blockers, proton pump inhibitors) may reduce absorption of cefuroxime.
- Increased effect: High-dose probenecid decreases clearance
- Increased toxicity: Aminoglycosides increase nephrotoxic potential