- 01792-220191, 09839141955, 06390845955
- SCO No. 2 & 3, Block-B;Office No.-249A; 2nd Floor, Motia Plaza Baddi-173205; Distt. Solan (H.P.)
- Home
- Injections
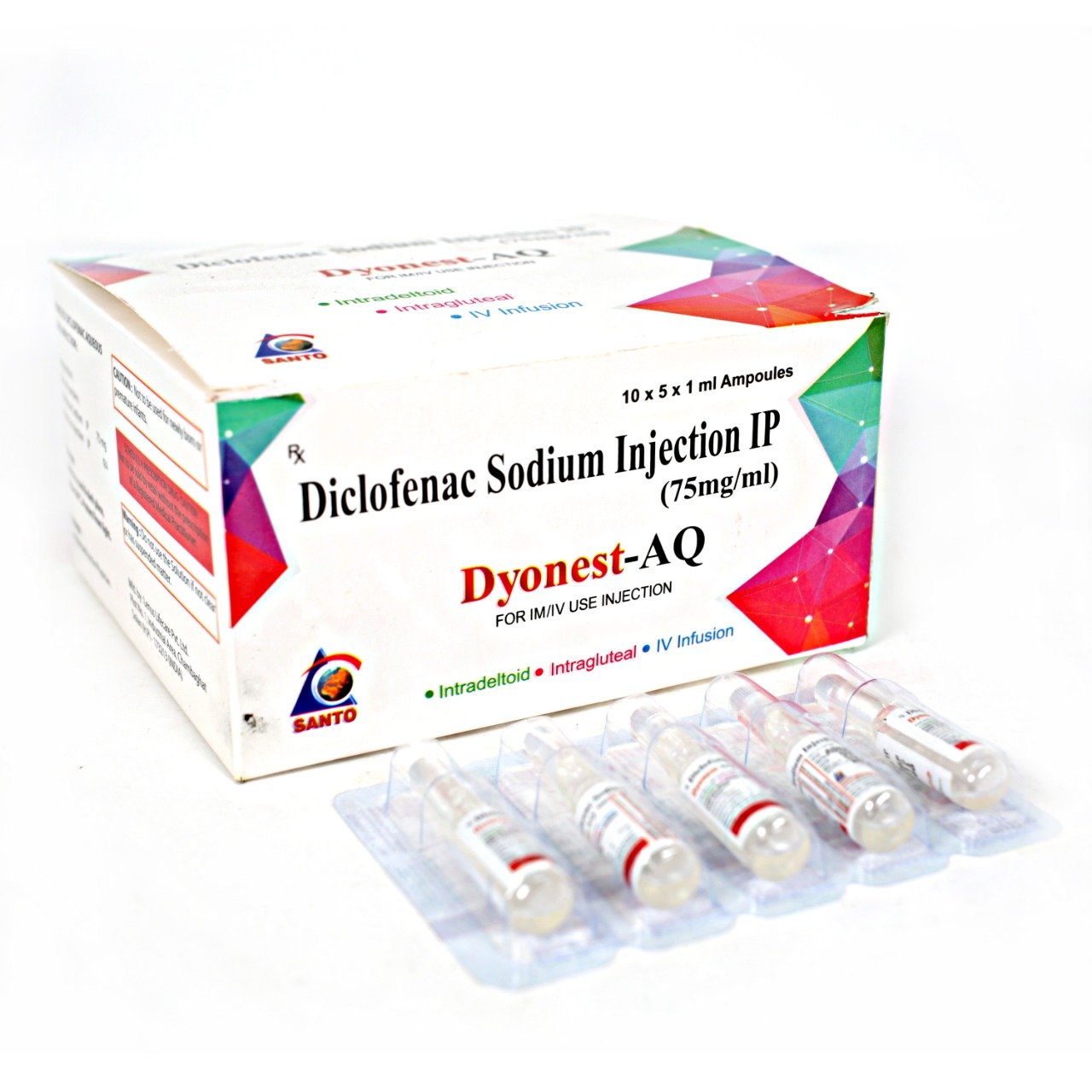
- DYONEST-AQ
DYNA-INJECTIONS
September 19, 2019
GRAVICARE
September 19, 2019DYONEST-AQ
| Brad Name | Dyonest-AQ |
| Composition | Diclofenac Sodium 75 mg/1 ml Injections |
Diclofenac Sodium 75 mg/1 ml Injection
Diclofenac Sodium 75 MG Injection is a Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) drug used to treat pain associated with conditions like Gout, Migraine, Rheumatoid Arthritis, sprains of muscles and joints and in mild to moderate fever in some cases.
- If you have an allergy to diclofenac or any other part of diclofenac injection.
- If you have an allergy to aspirin or NSAIDs.
- If you are allergic to any drugs like this one, any other drugs, foods, or other substances. Tell your doctor about the allergy and what signs you had, like rash; hives; itching; shortness of breath; wheezing; cough; swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat; or any other signs.
- If you are pregnant or may be pregnant. Do not take diclofenac injection if you are in the third trimester of pregnancy. You may also need to avoid diclofenac injection at other times during pregnancy. Talk with your doctor to see when you need to avoid taking diclofenac injection during pregnancy.
Dosage
Missed Dose
Overdose
Precautions
Before taking diclofenac, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to aspirin or other NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen, naproxen, celecoxib); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: asthma (including a history of worsening breathing after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs), bleeding or clotting problems, heart disease (such as previous heart attack), high blood pressure, liver disease, growths in the nose (nasal polyps), stomach/intestinal/esophagus problems (such as bleeding, ulcers, recurring heartburn), stroke.
Side effects
Upset stomach, nausea, heartburn, diarrhea, constipation, gas, headache, drowsiness, and dizziness may occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Remember that your doctor has prescribed this medication because he or she has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
This medication may raise your blood pressure. Check your blood pressure regularly and tell your doctor if the results are high.
Drug interaction
- Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor’s approval.
- Some products that may interact with this drug include: aliskiren, ACE inhibitors (such as captopril, lisinopril), angiotensin II receptor blockers (such as valsartan, losartan), corticosteroids (such as prednisone), cidofovir, lithium, methotrexate, “water pills” (diuretics such as furosemide).
- This medication may increase the risk of bleeding when taken with other drugs that also may cause bleeding. Examples include anti-platelet drugs such as clopidogrel, “blood thinners” such as dabigatran/enoxaparin/warfarin, among others.